AI agent vs AI model are two terms frequently muddled within artificial intelligence, despite their separate roles and functionalities. Clearly understanding this AI agent vs AI model difference not only helps us grasp each technology’s essence but also supports more effective AI application in practice, from product development to strategic planning, making the AI agent vs AI model comparison crucial.
What is AI model?
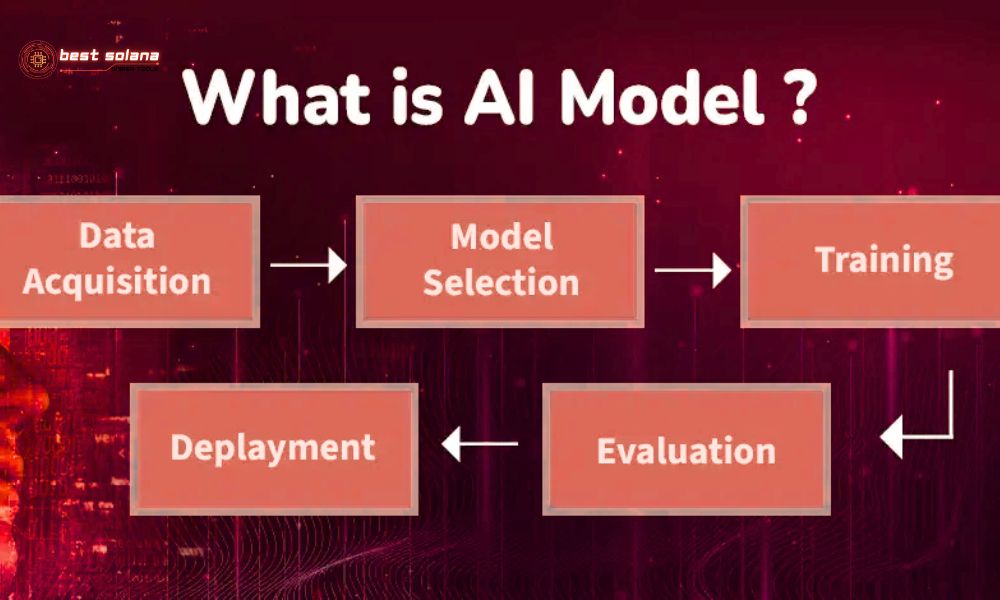
An AI model is essentially a program or algorithm trained on a large dataset to perform a specific task without being explicitly programmed for every scenario. It learns patterns and relationships from the input data to make predictions or decisions on new, unseen data. The discussion of AI agent vs AI model often starts with understanding the model’s foundational role.
Key characteristics of an AI model:
- Specialization: Typically designed to solve a specific problem, e.g., image recognition, language translation, market trend prediction.
- Learns from data: The quality and quantity of training data directly impact the model’s performance.
- Input-output: Receives input data and produces a corresponding output, e.g., an image as input, and the label of the object in the image as output.
- Not self-acting: An AI model itself cannot interact with an environment or proactively take action. It requires an external system to provide input and interpret output.
Examples of AI models:
- Large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3, BERT, capable of understanding and generating text.
- Image recognition models like VGG, ResNet, which can identify objects in images.
- Predictive models in finance and healthcare.
Imagine an AI model as a specialized brain, for instance, a translation expert proficient only in translating from language A to language B, or an artist specializing only in landscape paintings. They are excellent in their field but need someone else to assign tasks and use their work results.
What is AI agent? The intelligent acting entity
An AI agent is an autonomous entity capable of perceiving its environment through sensors, processing that information to make decisions, and then taking actions through actuators to achieve a specific goal. This is where the AI agent vs AI model distinction becomes very clear.
Key characteristics of an AI agent:
- Autonomy: Capable of operating independently without constant human intervention.
- Perception: Uses sensors to gather information about the current state of the environment.
- Decision-making: Based on perceived information and defined goals, the agent decides what action to take. This is where an AI model is often integrated.
- Action: Performs actions through actuators to change the state of the environment or achieve its goals.
- Goal-oriented: All actions of an agent are aimed at accomplishing one or more specific objectives.
Examples of AI agents:
- Self-driving cars: Sensors are cameras, lidar; the decision-making unit (which may contain multiple AI models for lane detection, obstacle recognition) controls the steering wheel, brakes, accelerator (actuators) to navigate safely to a destination.
- Virtual assistants (like Siri, Alexa): The microphone is the sensor, natural language processing (using an AI model) understands requests, and the speaker or device command execution is the actuator.
- Smart robot vacuums: Sensors detect dirt, obstacles; the processing unit plans movement; motors and brushes are actuators.
- Intelligent non-player characters (NPCs) in games: Perceive player actions, game environment, decide on reactions, and perform actions within the game.
An AI agent often contains one or more AI models internally as its “brain” or “specialized tools” to support its perception and decision-making processes. The debate of AI agent vs AI model isn’t about which is better, but how they work together.

Comparing AI agent vs AI model: Core distinctions
| Feature | AI Model | AI Agent | |
| Main Purpose | Predict, classify, generate data based on patterns | Achieve specific goals in a given environment | |
| Components | Algorithm, training data | Sensors, decision-maker (can include AI model), actuators | |
| Interactivity | Passive, receives input and gives fixed output | Active, continuously interacts with the environment | |
| Action Capability | Cannot act on its own | Can perform actions to change the environment | |
| Scope | Narrow, specialized for a task | Broader, integrates multiple capabilities to achieve goals | |
| Example | GPT-3 model, facial recognition model |
|
The synergistic relationship between AI agent and AI model
An AI model is a crucial component, often the “heart” or “brain” providing intelligence to an AI agent. The agent uses the model’s output (e.g., predictions, classifications) to make decisions and take action. This interplay is key to understanding the full AI agent vs AI model picture.
An AI agent can use multiple different AI models. For example, an autonomous delivery robot (AI agent) might use one AI model for path recognition, another for package identification, and yet another to optimize its route.
The AI model provides “intelligence,” while the AI agent provides the “body” and “ability to act” to apply that intelligence in the real world or a virtual environment.
In other words, if an AI model is a consultant (e.g., a market analyst), then the AI agent is the chief executive officer (CEO) who uses that consultant’s advice, combined with other information, to make business decisions and execute strategies. The effectiveness of an AI agent often depends on the quality of the AI model it employs.
Why does this AI agent vs AI model distinction matter?
Clearly understanding the difference between an AI agent vs AI model offers several benefits:
For developers: Helps in choosing the right tools and architecture. They need to know when to just build a specialized model and when to develop a complete agent.
For businesses: Assists in making more accurate AI investment and application decisions. They can determine if the solution they need is a data analysis model or an automated agent system.
For end-users: Provides a more realistic view of AI’s capabilities, avoiding unrealistic expectations or unfounded fears.
Clarifying these two concepts also promotes the development of the AI industry in a more transparent and accessible direction. The AI agent vs AI model discussion is fundamental to this clarity.
An AI model is the knowledge base, providing analytical and predictive capabilities, while an AI agent is the acting entity, using that knowledge to interact and achieve goals in an environment. Grasping the nuances of AI agent vs AI model is key to unlocking AI’s full potential. Keep following Best Solana Sniper for more exciting and useful tech insights!